Any discussion of Bigfoots’ existence is likely to create a range of emotions among the public from absolute denial to complete and unquestionable belief.
Somewhere in between are the murky waters of unanswered questions; “how do they survive winters?” “Are they related to us?” “Why don’t we run into them more often?”
In this paper, I hope to shed some light onto the potential answers to those questions and more. After all, just like us, Bigfoots’ existence depends on having ancestors. In this paper, I will explore their possible lineage and evolutionary adaptation.
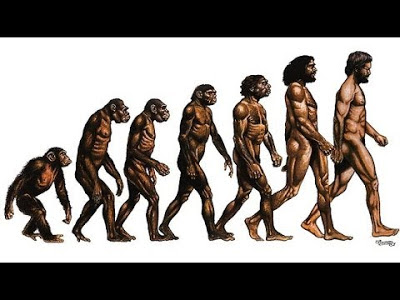
This evolutionary lineup of man (above) is not really accurate. Throughout man's development to what we are today, there was interbreeding among sometimes fairly disparate relatives. Only recently we discovered that today’s Homo sapiens carry DNA of Denisovans, Neanderthal and another, as of yet unnamed, archaic man.
This introduction of other chromosomes might have helped us to be stronger in certain arenas, and more vulnerable and disease-prone in others. But, they also helped us make a leap from our African origins to northern climate adaptation very quickly. For instance, Neanderthal genes likely helped our coloring to handle less sunlight by developing more vitamin D when we did encounter sunlight and Denisovans made it possible for today's Sherpa to live at high elevations and tolerate it readily, as well as cold tolerance for the Inuit People.
What we have to wonder is where do today's Bigfoot stand in this lineup of man in both "archaic" and "modern" forms, as well as races within each branch? Do we share ancestors? Do we share genes? Is there any chance we ever mated in the past and produced offspring?
Pushing aside the notion of Bigfoot as an alien hybrid, Nephilim, worker race designed by aliens, transdimensional, and other extraordinary claims, my observations and conclusions herein will be utilizing known entities here on Planet Earth. I am going to following along the lines of Occam’s Razor, a concept which basically states that the most practical conclusion is the most likely.
Denisovans
We know very little about Denisovans as a people. We only learned of their existence in the twenty-first century.
The fragments of their remains were found in Siberia in the Altai Mountains in the Denisova Cave. This cave was also inhabited at various times by them, Neanderthal and Homo sapiens.
We also know that their DNA has shown up in our populations around the world in certain areas, like Neanderthal DNA has in Europeans.
As we study the chromosomes they passed down to today's modern people, we learn much about what they were evolved and acclimated to. Studying these patterns and characteristics, as well as locations around the world, I have come to my own personal conclusion as a researcher that -
The fragments of their remains were found in Siberia in the Altai Mountains in the Denisova Cave. This cave was also inhabited at various times by them, Neanderthal and Homo sapiens.
We also know that their DNA has shown up in our populations around the world in certain areas, like Neanderthal DNA has in Europeans.
As we study the chromosomes they passed down to today's modern people, we learn much about what they were evolved and acclimated to. Studying these patterns and characteristics, as well as locations around the world, I have come to my own personal conclusion as a researcher that -
Bigfoot (and its races*) are the people descended from Denisovans primarily (with the possibility of some ancient hints of Neanderthal and Homo sapiens DNA tens of thousands of years ago, much as we carry some Denisovans and Neanderthal today in tiny percentages).
Please keep in mind that this is a very heated topic as to the origins of Bigfoot, and these conclusions I have made I will support throughout this paper.
I began this voyage into Bigfoots' ancestry by rather simple means. In order to show that they are a feasible population, I had to find out where they descended from, as they are divergent enough to not be Homo sapiens, but a fellow man of some type. As I have personally determined they are not here by magical means, I had to look at what we have here on Earth to explain them.
First, I asked myself where is evidence of giants in America? Well, it was found in old documents of dug up skulls and skeletons of enormous size from ancient times on our continent.
I then began to wonder about Native legends of giants and wars with giants, killing off giants, driving giants away into the wilderness, and began to see correlations that needed to be explored more deeply.
What other giant man do we know of from man's past that is scientifically documented? Giant molars found belonging to Denisovans had me wondering. As much as Bigfoot appeared almost Neanderthal-like in body proportions and skull, Bigfoot are much taller. Who do we know from that archaic time period who had giant characteristics and adaptations for cold climates? Denisovans had huge molars (LINK) and lived in a cold northern climate.
First, I asked myself where is evidence of giants in America? Well, it was found in old documents of dug up skulls and skeletons of enormous size from ancient times on our continent.
I then began to wonder about Native legends of giants and wars with giants, killing off giants, driving giants away into the wilderness, and began to see correlations that needed to be explored more deeply.
What other giant man do we know of from man's past that is scientifically documented? Giant molars found belonging to Denisovans had me wondering. As much as Bigfoot appeared almost Neanderthal-like in body proportions and skull, Bigfoot are much taller. Who do we know from that archaic time period who had giant characteristics and adaptations for cold climates? Denisovans had huge molars (LINK) and lived in a cold northern climate.
I went from trying to prove Bigfoot is feasibly a citizen of Earth and the human race by finding a lineage studying the hints of DNA in our population, locations around the globe, as well as Bigfoot's behavior and characteristics to make a logical conclusion about their lineage.
Note: My conclusions may not be at all what the reader has come to, but I hope to offer enough supporting evidence and logical conclusions that this concept might take hold in the mind and create pursuit by others into the origins of Bigfoot.
At times, this journey has been stunning in that every new thing we learn about Denisovans so clearly correlates with today's Bigfoot that I shake my head and am amazed at how the pieces were before us all this time.
Now, let’s go over all the features to show how I came to such a conclusion.
Evolution is an ongoing process. If you and I evolved from an archaic form, such as Homo erectus, then Bigfoot is now the evolved from of a prior archaic self.
We cannot truly call them an archaic, although their features remind us of our own early beginnings with a powerful build, prominent brow ridge, and stocky shape. They are a contemporary of their ancestor.
In my prior paper (LINK) about the slope-headed people of early North America, I cited a skull found in Humboldt sink and studied by anthropologist Eric Reid and other anthropologists with a few different universities.
This skull he referred to as “otamid” or “archaic” with features from a prior earlier man. Reid noted os inca bones (interparietal bones that can cause a pointed look to the back of the head) and a jaw built to be carnivorous (versus omniverous like we are). It was also of an exceptional size.*
(*Feel free to contact me by email ghosthuntingtheories@gmail.com for a copy of the full report Eric Reid published, as it was taken down from online at an educational paper scanning site after the publication of my article).
He also compared it to other "otamid" skulls found around the world. Such skulls were described in the Yaghan tribe at the tip of Tiera del Fuego in South America to Pericue of Baja, California and Karankawa coastal Indians of Texas (all extinct tribes now).
Victoria, Texas - land of the extinct tribe of Karankawa
This odd skull above from the Humboldt Sink didn’t belong to any known Amerindians was not only ancient, but showed another race of man here on the continent long ago. A race with massive skulls.
Repeatedly the skull shape attributed to Bigfoot has been large, prominent brow, powerful jaw, and pointed head. These are also features that were emulated by Northwest Salish Indians of America, and many Native people of South and Central America by binding the skulls of the youth. This is also the description given to ancient giants’ skulls found around the world.
As well, Natives have reported cannibalistic giants from very long ago around the entire globe. What we know of Denisovans so far is from examining the DNA extracted from only small finds, molars, finger bone. What we do know of the molars are that they were exceptionally large. (LINK) The size of the teeth suggests that the Denisovans had very large jaws and more likely resembled Neanderthals than humans. A powerful jaw could infer that their diet was more carnivorous and the powerful jaw would be important for the break down and digestion of meat.
We have now established contemporaries of modern man (Homo sapiens date back 100,000 to 200,000 years approximately), and these contemporaries had different attributes, including a jaw that showed they were carnivorous which is a predator, basically. The very way they would go about hunting and eating would be as predator to prey. This, in itself could have caused some issues with modern man who would not tolerate cannibalistic tendencies. And, ultimately may have led to the legends of Native People killing off and driving off the giants who even today remain reclusive in lands that we consider fairly inhospitable, but they were completed adapted to survive in.
BODY FRAME/PROPORTIONS
The legs of a Bigfoot are proportionally shorter than the long body. But, if you match up arm and leg length, you find them similar. If you and I were to try to walk on all four, our long legs, would make our butt hike up in the air and be quite awkward.
If we had, however, a long body, and arms and legs of similar length, walking on four would be actually easy and practical. With long enough arms, we could even see well as we walk on all four -
Bigfoot is often reported to easily and readily get onto all four and gallop as if their hip joints are very loose and flexible. Some compare it to the way a rabbit leaps and launches.
In our own shoulders, we have a rotator cuff that allows us to move the arm around in full circle. Our hips, however, are not built this way. You and me evolved to walk across the plains, one foot in front of the other on relatively flat straightforward ground.
But, what if we evolved to climb a tree or a mountainside? We would have flexible hips like a chimp or a Bigfoot who climbs hills rapidly and often.
Denisovans were adapted to high altitudes. We know this, as the Sherpa people of the Himalayas have a chromosome they inherited from their Denisovans DNA (LINK) that allows them to readily tolerate high elevations without the clotting and breathing issues we flatlanders have.
So, we know that Denisovans (outside of Africa long before we Homo sapiens left that continent) had already adapted nicely to high elevations and the climate and food supply within which would be meat and fish more so than short-lived plant life.
Inuits today have been gifted a cold tolerant chromosome from their Denisovans DNA, as well. The Yaghan Natives of the tip of South America were said to sleep out in the open in the cold and bathe their babies in the arctic-temperature water without any issues with cold intolerance. They were also reported to have a different shaped skull than other Native People. We can easily assume that they carried Denisovans DNA. That Denisovans DNA seemed to have circumnavigated by sea, an interesting realization. Coastal people seem to carry the gene, as well as high elevation people in Asia.
Why are Bigfoot so tall? That is yet another adaptation. But, what we know about cold climate adapted Homo sapiens is that they are often Neanderthal-like in compact, shorter proportions.
But, we also know that within Africa, there are tribes who are pygmy and ones who are very tall.
Why would a Bigfoot ancestor grow so tall? More surface area on the body might be the key. We know that polar bears have black skin and translucent hair. Might this help to retain a heated body if there is more dark skin available to heat under the sunlight at high altitudes? It also might be as simple as body frame. To have the massive muscles necessary to live in high altitudes and climbing, one would need a substantial skeleton to support that.
What we know about living in a high altitude, besides the need to perhaps possess a barrel-shaped chest, is that massive muscles would be a natural adaptive aspect. If you have ever been hiking or jogging and then you go to the mountains to do hiking on inclines and declines, you know feel it the next day. You think you use muscles a lot to propel yourself on flat ground, but once you start billy goating, you realize exactly what muscles would be utilized by a mountain-adapted person - the calf muscles, hips and buttocks.
Why aren't sherpas particularly tall and yet they carry Denisovans DNA and live in mountainous regions? Their average height is 5'6", but then remember their relationship to Denisovans is very distance, having tens of thousands of years of Homo sapiens DNA, especially Asian (shorter height) DNA to interbreed with.
The Sherpa do, however, have adaptation for high elevations and cold, but they also can carry extraordinary loads. (LINK) A typical Sherpa roams the Himalayas carrying a load that weighs more than he does. Scientists wanted to know how this was humanly possible, so they set up a laboratory along one of the busiest Sherpa routes in Nepal. The study found ... when a porter carried a load, his or her metabolism increased, but only about half as much as a European's would. This very efficiency is likely how they are able to
It would seem that Bigfoot's very metabolism might be based upon a gene from their possible Denisovans' heritage that allows heavy work loads and massive muscles with less need for calories than we would. They are an efficient machine. Just to simply have the massive musculature on a weightlifting athlete in a Homo sapiens with no Denisovans DNA would take enormous caloric intake (3000 to 8000 calories a day for an average height male weightlifter).
It would seem that Bigfoot are not just tall, powerful, with different skeletal proportions and more flexible joints, but their very metabolism may allow them to be even more powerful than thought, as well as less calorie and oxygen needs than we have.
HAIR

(photo thanks to MK Davis)
It takes approximately 100,000 years for an evolutionary change to show in man's appearance. Homo sapiens have been around 100,000 to 200,000 years in Africa (the form of modern man we are now). The changes we had were divergent enough from our prior form that we received a whole new name for our kind - Homo sapiens.
Interbreeding for the past hundreds of thousands of years, leaving Africa, mating with other forms of man, adapting to new locations and breeding with a stable farming community allowed for many races within our family to develop.
If Bigfoot are of Denisovans' ancestry, then their move down from the highest peaks in the world to forests might have caused an adaptation to more dark hair and less of the lighter tones that were adaptive for snowy mountains and little sunlight. In the dappled forests, the adaptation to dark hair would help them to disappear in the darkness of a forest.

Above, there is an example from Fred Kanney's video, "On the Hill." He used a great technique I recommend to pan back and forth 180 degrees slowly because as you move and look away, the Bigfoot who might have been caught by surprise, will move to get out of view, but when you pan back, you find later on while reviewing the video that it moved. In this case, the fellow tried to stay very still like a statue (their #1 protective mechanism, as they understand movement will give them away). Only, this gentleman didn't realize that the wind might give him away and a tuft of hair rose up in the breeze.
Take note of how his deeper color helps him to become one with the forest.
Reported hair colors for Bigfoot vary as much as any human. There are blonds, redheads, brunettes, very dark black hair, and even gray. What seems to be apparent from observations of the hairs and in the field is that the hair might have a translucent quality. That translucence could benefit them greatly in not being detected. So long as they stand very still when you are looking around, you are not likely to see them. They absorb light and dark like the rest of the forest. Some hair samples studied appear to have sensory cells in them. If that is true, then their entire body could be an extra sense of a sort. I discussed this much in my paper about Bigfoot’s hair (LINK).
The hair covering, as well is an important climate adaptation for the Denisovans. The aborigines have facial hair and hairiness in a way that was not seen by other Native people around the world. They also carry a tiny fraction of ancient Denisovans DNA.


Islanders of the South Pacific, especially the Solomon Islands, have blond hair within their population but recent DNA studies reported it was not from European blond hair lineage, but some other source. What was that source?
Well, these people all carry ancient Denisovans DNA like many Europeans carry Neanderthal. We can take it to mean that Neanderthal might have given us blond and red hair, and Denisovans might have also, as they were northern/cold climate evolved.
Let's look at another cold-weather acclimated creature upon the earth- the polar bear. Their hair is actually translucent (LINK) and their skin is black. Interestingly, polar bears in a compound were turning green and workers wondered what was going on. It ended up the hairs had algae on the outside of them. This translucent quality actually makes the hairs rather adaptive to their surroundings and to dirt, mud, and other surface agents.
Uniformly, the majority of witnesses report Bigfoot having a blue-gray tinge to the skin, from light to dark, mostly dark, however. This blue gray appearance might correlate with a human who has adapted to cold climates. With fewer capillaries near the skin surface that could create frostbite situations and make one sensitive to cold, the surface skin would appear thick, tough, and bluish gray. The very qualities described fit an adaptation for cold. (LINK to my article on Bigfoots' Skin)
Early Bigfoot researchers pondered that Bigfoot migrated, but there no evidence of long distance movement of them seasonally and most habituators (those who live on a property and interact with the Bigfoot who also use that land) report them on the properties even in the wintertime. Given that Bigfoot-like beings are reported in cold and mountainous regions, we can make a logical guess that they were adapted/evolved for northern and high altitude climates.
BREEDING
The majority of anthropologists believe Neanderthal and Denisovans to be extinct. Well, we could say Cro Magnon is extinct, except here we are today, the walking talking result of their existence. So, the DNA continues on. We no longer have the old version of us running around, so we can call them “extinct” and if Bigfoot is the descendant of Denisovans than, yes, technically Denisovans are extinct, but their modern version might be running around our woodlands today.
The question is; during a bottleneck in evolution where we could no longer breed with these other types who shared an archaic past with us, did they manage to continue on without utilizing us as a breeding pool? We managed to breed quite fine without them as our populations took over Europe, Asia and other regions.
After all, we may have mated with archaics when we could, but it was precarious at best. The result of a Neanderthal-Homo sapiens mating created sons who were almost surely infertile. The hybrid daughters, however, could mate and continue passing on the genes which is how we have them today.
What if Denisovans mating with Neanderthal or with themselves created fertile sons and daughters? The ones who mated among themselves would have survived into today.
If you look at Homo sapiens, we don't look terribly close to Neanderthal any longer, as we have mated among ourselves since the time of interbreeding with other archaics was no longer possible. Today, we carry Neanderthal genes, but we are rather dissimilar in many ways after tens of thousands of years.
The same goes for aborigines, Melanesians and others who carry Denisovans genes. They barely have any traces of their ancestors' in their appearance, save perhaps the rocker jaw and pentagonal-shaped skull, some other chromosomes that allow for high altitude adaptation and other Denisovans' traits.
But, Denisovans who continued to mate with their kind perhaps distant traces of Neanderthal or Homo sapiens, might have left them with very faint resemblance to us today, as well. We would be distantly in their gene pool, too long ago to see quite clearly today.
Even today we can see a human with a prominent skull, Neanderthal-like build or face and see a bit of the history in them. Such variations in skull shapes and traits can pop up.
The same could be reported for Bigfoot who have strongly Homo sapiens-like features to almost seem like one of us with hair all over and others look closer to their own interbreeding with very Denisovans-like features.
Our time line for our own evolution as Homo sapiens might not be very accurate. It almost never is once we find more evidence. Take for instance, Neanderthals. We assumed we did not have successful mating with them, and yet here we have found their DNA in mostly European Homo sapiens. Then, Denisovans came along, another man we didn't know about and - voila - we have their DNA found mostly in Melanesians, aborigines and sherpas. So, this time line of archaics being extinct 30,000+ years ago is not based on any written text, as no written texts existed back then.
As well, we have finally accepted that Neanderthals and Denisovans, who were all over Europe and Asia long before Homo sapiens spilled over the borders of Africa, managed to not only adapt to their environment, but show very high signs of intelligence, likely more so than our own at the time.
Neanderthal’s brain capacity was even larger than ours and Denisovans were found to have tools of such high skill long before we did that, we must accept they were ahead of us tens of thousands of years ago.

This Denisovans sewing needle (above) was found to be not only an amazingly crafted 3” needle made from bird bone, but was high up in the Altai Mountains in Siberia (there’s those mountains again). (LINK) This needle is also 50,000 years old!


This Denisovans bracelet above (amazingly crafted) was 40,000 years old!
LEGENDS OF GIANTS
For Bigfoot to have existed all this time, he must not only have ancestors, but our people must have encountered his ancestors. In my voyage to discover Bigfoots’ daddy, I pondered North America. The only possible ancestor was from the bones of other giants found here, the most logical lineage. Native people and religious texts have accounted for this race for tens of thousands of years and we have thought of them as fanciful stories. It’s time to look at Native Legends for their extraordinary passage of knowledge to further generations.
Man fairly recently in the scheme of things began to document his history in writing. There is nothing to say that these types of "archaic" man weren't around say 10,000 years ago and among the people of the time, but simply no written documents were kept, only spoken legends.
Let's look at the spoken legends from around the world that speak of giants among man:
Chad Africa - They have legends of their ancestors being giants taller than trees.
Nevada Paiutes Tribe - Tales of red-haired giants cannibalizing their people and the tribe finally cornering them in a cave and burning them.
Peru - Legends of giants coming ashore and eating their people and causing torment.
Sicily - Laestrygonians. This was a tribe of giant cannibals from Greek Mythology.
Aborigines - Tale of two women luring a cannibalistic giant into a cave to burn him alive.
Ireland - They called them Fomorians, a supernatural race of giants and sea raiders.
Easter Island - Talk of the long-earreds being forced into a trench and burned.
Germany - Many of their myths involve giant tribes.
Greece - Titans were an giant elder race of gods.
Scandinavia - Talk of giants called "Jotunn," a banished race of giants.
Native American - legends often speak of the giants who lived there before their ancestors arrived.
The mythology of many cultures from China to Russia, Tibet to Africa, the South Pacific and even Native Americans involve talk of giants. When giants have existed in the "myths" of many cultures around the world, one has to wonder what we encountered in our past that created oral legends to be passed down. Perhaps it was done to always remind mankind of the giants who were among us. Religious texts of angels coming down and mating with our beautiful women to create the Nephilim might even be a distant story passed down about the Denisovans and the Homo sapiens.
BIGFOOT DESCRIPTIONS/BEHAVIOR
Their ability to live in hillsides and steep inclines is their strength. They can scramble up and down hillsides with incredible speed, given their longer body, shorter legs and flexible hips and knees. They also can stay up there where they can lift a heavy rock and slam it down on another to make an echoing sound through the ravine and signal others.
When necessary to ward others off without harm, they utilize their ability to create infrasound. Others of their kind can sense this and know that one of their own feels threatened. Infrasound can carry long distances which is ideal for a mountainous people. A Homo sapiens human is capable of infrasound and when studied, it was found his vocal chords were extra long. A 7-9 foot tall human relative could certainly make infrasound and utilize it, as well.
They imitate the sounds of every animal in the woods, sometimes even tagging on a series of calls after a bird. They rile up the packs of coyotes to cover up the sounds of their hunts and run with them in a kind of symbiotic relationship involving the hunters and the scavenger coyotes. There are certain consonants the Bigfoot have difficulty pronouncing which gives us better insight into their lips and tongue, palate and more. (LINK to my post on Bigfoot language). They utilize the wildlife readily, from chasing down deer into areas where others lay in wait to catch them, to counting on the crows and blackbirds to warn them like a doorbell that someone is coming close. These birds are known to make three calls when they sight us and then many calls in a row when we are coming near.
Bigfoot remains mythical so long as we don't explain their potential origins. I entered research studying language and potential intuitive skills, expanded my focus into guidelines for habituation sites and helping field researchers adapt their approaches in the field as it's happening, and came to realize that, until we explain how they exist, Bigfoot is infeasible to most people who have not actually witnessed one.
MK Davis YouTube Channel (LINK)
MK Davis did a great job on this video breakdown and he has only just started to look it over but what's in it reiterates my own theory on the Bigfoot being adapted/evolved for high elevations and cold climates. Their hips are more like the rotator cuff of our shoulder. Their legs are shorter in proportion which means they can go on all four without their ass in the air like we do with our long legs. They have gray blue skin that has no surface capillaries to freeze, but more keratonized and tough for colder climates. Their hips allow them to paddle their legs up mountainsides, over varying terrain and rocks without issue, unlike us. We were adapted for walking across plains with forward facing legs. Now, look at a chimp in the zoo hanging from a tree. They pull a leg up and use the toes to help pull them onto the limb. Our legs want to go forward, theirs can rotate and go up to climb. A Bigfoot, adapted for mountainous regions, would need that same flexibility of the hip. This would also mean that as they walk, knees are slightly bent, center of gravity is low and they have no head bob because of this (runway model's walk). With all these considerations, my #1 candidate for Bigfoot's ancestor is Denisovans, a large human who had a gene for high altitudes.
Depending on Homo sapiens isolated locations, climates, diet, and interbreeding in closed communities, we have managed to create many races among our people. The same can be said of Bigfoot.
If we want to understand how Bigfoot could be Denisovans, let’s do the logical thing and see if today DNA of Denisovans shows up in people of various regions around the world and if in those same regions today Bigfoot or Bigfoot-like people are seen.
Inuits carry some Denisovans DNA. These Native People of the Arctic Circle are a hearty and well-adapted people. (also included with Inuits, we can likely add Pericues, Karankawa and Yaghan of the Americas who showed strong evidence these coastal people were of another lineage than Amerindian/Asian origin).
In North America, we also have reports of what I like to call "Homo clivus frons" (sloped forehead people). Here, we call them a few different names, but most popularly Sasquatch and Bigfoot. Reports of them are especially strong in the Sierras, Cascades, Rocky Mountains, and Appalachia.
The aboriginal people have been found to be the longest singularly isolated race of people on the earth. Their remote location made it possible for them to have tens of thousands of years on the continent without outsider intrusion or influence of others' DNA for tens of thousands of years.
The aboriginal people also carry ancient Denisovans DNA in their makeup. As well, on their continent, there are Native legends of giants and today reportedly what could be a race within the Bigfoot family, referred to as "Yowie."
"Yeren" - Mountainous China
"Alma" - Siberia
Sherpas - "Yeti" - Himalayas
From the mountainous region of China's borders with Himalayas, Siberian Altai mountains and Mongolia, we find the original remains of Denisovans in the Altai Mountains.
In these mountainous cold regions where Denisovans were settling and making sophisticated tools tens of thousands of years ago, we today have sightings of "Alma" (Siberia), "Yeren" (China) and "Yeti" (Himalayas). The Sherpa people share DNA with the Deniovans from long ago and that very DNA helps them to tolerate high elevations.
In these mountainous cold regions where Denisovans were settling and making sophisticated tools tens of thousands of years ago, we today have sightings of "Alma" (Siberia), "Yeren" (China) and "Yeti" (Himalayas). The Sherpa people share DNA with the Deniovans from long ago and that very DNA helps them to tolerate high elevations.
Just as we could go around our globe and find isolated indigenous people who are various races of Homo sapiens family, we could go around the globe and locate the races of Denisovans (if my hypothesis is accurate).
Breeding naturally brings recessive traits and dominant traits into play and we can created billions of different faces and coloring around the globe. So it would seem with the Bigfoot who are often reported to have a face thrust forward almost muzzle-like or looking extremely Homo sapiens. Some have broad noses and dense dark hair, some have slender noses with sparse hair. All these variations are normal within isolated breeding groups and those that venture out and breed with isolated groups.
For you and me, we can travel the world by ship or plane and meet others, mate with other races quite readily. For the Bigfoot family, it is a matter of great isolation, even within one content the clans are rather isolated and have different characteristics. This is prominent in the United States where some regions see very tall ones, others very aggressive ones, some with a good deal of white-haired ones within a clan's range, hairier ones, less hairy ones, ones that look more like us, others that seem almost primitive-like with their features.
Denisovans also had a gene to help them adapt to new environments, so a mountain-evolved people could take to the South Seas and have no issues with adaptation, and different adaptations and "looks" on various contents over tens of thousands of years. (LINK)
For you and me, we can travel the world by ship or plane and meet others, mate with other races quite readily. For the Bigfoot family, it is a matter of great isolation, even within one content the clans are rather isolated and have different characteristics. This is prominent in the United States where some regions see very tall ones, others very aggressive ones, some with a good deal of white-haired ones within a clan's range, hairier ones, less hairy ones, ones that look more like us, others that seem almost primitive-like with their features.
Denisovans also had a gene to help them adapt to new environments, so a mountain-evolved people could take to the South Seas and have no issues with adaptation, and different adaptations and "looks" on various contents over tens of thousands of years. (LINK)
CONCLUSION
I do not profess to carry a scientific degree, but a great deal of knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and anthropology; all based on a lifetime of interested study.
I also possess a very practical and logical nature. I look at what our world has here that is accounted for and with those known elements, how can I explain the existence of the Bigfoot People?
For many year, I have studied Bigfoot with other co-researchers with focus on their language, habits, relationships, and habituation site interactions.
I began my study on practical aspects of Bigfoots' day to day life and then finally extended it into pondering their origins to explain their place here on the planet.
One thing led to another until it seemed extremely clear to me how they got to be where they are, act as they do, and their lineage.
I plan to upload this paper into Academia.edu site and keep it out there for public viewing to allow others to peruse it, consider it, and perhaps even do their own research on aspects of this hypothesis.
Are the Bigfoot-types around the world the descendants of Denisovans? For me, it is a very clear possibility and #1 on the list of suspects. They are in the right locations, their DNA shows up in the right populations, they have enough isolation, their relationship with our kind appeared to have been one of battling, forcing them to go retreat into areas that they are adapted for, and the descriptions of their looks and behaviors are suitable for being Denisovans in origin.
My only caveat to this notion of Bigfoot as descendants of Denisovans is if the one unknown man might be the ancestor. The unknown man was found in the DNA of South Pacific Islander people. They have yet to find this man from our history and, although they could be the distant parentage, the reasons I chose Denisovans was their acclimation to high altitudes, cold weather, need for body hair, proportions, and where their DNA shows up in places that Bigfoot and Bigfoot-like people are seen today.
And, if you wonder how a branch of humankind could be under our radar into modern times, just have a look at this tribe on the Peru/Brazil border found in the 2000s -
MORE INFO:
Homo sapiens evolutionary process (LINK)
Denisovan, Neanderthal DNA in populations (LINK)
Nature Magazine about Denisovan DNA (LINK)
UPDATE: Two skulls found in China might be Denisovans - DNA testing underway (LINK)
Reports of Bigfoot-like 8-foot tall beings with brown and black hair climbing Mt. Popocatepeti at amazing rates of speed and agility rather confirms the concept of a mountain/high elevation-adapted man. (LINK)
Want to test your DNA? Compare DNA testing sites to find the best one - HERE.
Denisovans in Tibet article - HERE
Man with oldest DNA lineage in the United States, found his ancestors arrived to America via the Pacific Ocean and South America! LINK
Article from Nature about Denisovan-Neanderthal hybrid found. LINK
Humans and Neanderthal shared a mystery relative. LINK






















interesting blog post!
ReplyDeleteOne question. You wrote: "The result of a Neanderthal-Homo sapiens mating created sons who were almost surely infertile. The hybrid daughters, however, could mate and continue passing on the genes which is how we have them today."
Why would the male offspring be infertile? If you mentioned it elsewhere in the blog, I missed it.
-Allan, a.k.a. "RocKiteman" & "Kite-Squatch"